Alternator and Synchronous Generator Formulas & Equations
The following synchronous generator & alternator formulas and equations can be used to design, simplify, and analyze the basic AC generator circuits to determine the generated voltage and EMF, speed & frequency, efficiency, voltage & current, generated power and losses, etc.
EMF Equation of Synchronous Generator
RMS value of generated EMF per phase
VRMS = 1.11 x 4fΦT
VRMS = 4.44fΦT Volts
Actual generated voltage per phase
VPH = 4.44 Kc Kd f ΦTPH
VPH = 4.44 Kf Kc Kd f ΦT Volts
Where:
- V = Generated voltage per phase
- KC = Pitch Factor or Coil Span Factor
- KD = Distribution Factor
- Kf = Form Factor
- T = Number of turns per Phase
- f = Frequency
Output Electrical Frequency & Speed:
![]()
Where
- fe = Electrical frequency
- Nr = speed of rotor in RPM
- P = Number of poles
Voltage Generated:
Ea = KΦaNs
Where
- K = constant representing the construction of the machine
- Φa = magnetic Flux per pole of the rotor
- Ns = synchronous speed of the rotor
Total Phase Voltage:
VΦ = Ea – jXsIa – RaIa
Where
- Xs = Synchronous reactance of machine
- Ia = Armature current
- Ra = Armature resistance
Three Phase Terminal Voltage:
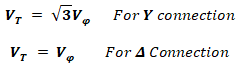
Power of Synchronous Generator:

Where
- Tapp = Torque applied
- Tind = Torque induced in rotor
- ωr = mechanical speed of rotor
Voltage Regulation:
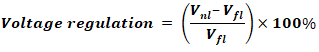
Where
- Vnl = Voltage at no load
- Vfl = Voltage at full load
Efficiency:
η = (POUT / PIN) * 100%
PIN = POUT + PCu + PIron + PMech + PStray
Where:
- η = Generator effeminacy
- PIN = Input power
- POUT = Output power
- Cu + Iron + Mech + Stray = copper, iron, mechanical & stray losses in a generator.