Electrical Transformers: How They Step Up and Step Down Voltage
Electrical Transformers are devices that are used to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. They are an essential component in the electrical power distribution system and play a crucial role in the transmission and distribution of electricity. One of the most important functions of an electrical transformer is its ability to step up or step down voltage levels. In this article, we will discuss how electrical transformers step up and step down voltage, and the underlying principles behind these processes.

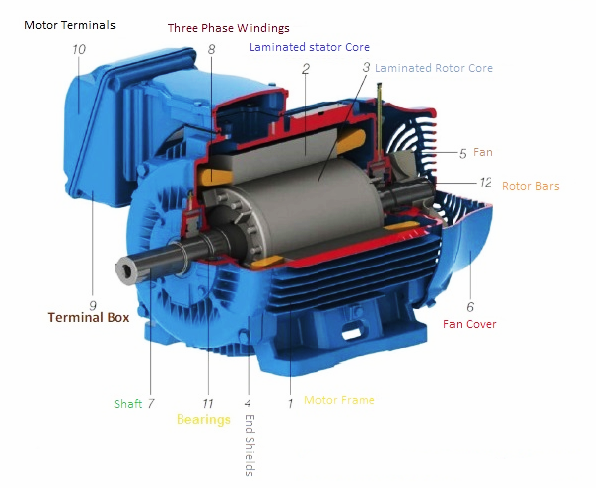
An electrical transformer is made up of two coils of wire, known as the primary and secondary coils. These coils are wrapped around a core, which is typically made of iron. The primary coil is connected to the source of electrical power, while the secondary coil is connected to the load. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary coil, it creates a changing magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary coil. The voltage level in the secondary coil is determined by the ratio of the number of turns in the primary coil to the number of turns in the secondary coil, known as the turns ratio.
When the number of turns in the secondary coil is greater than the number of turns in the primary coil, the transformer is said to be stepping up the voltage. This is known as a step-up transformer. The voltage level in the secondary coil is higher than the voltage level in the primary coil, which allows for the transmission of electrical energy over longer distances with less loss. This is why step-up transformers are commonly used in the transmission of electrical power over long distances.
On the other hand, when the number of turns in the secondary coil is less than the number of turns in the primary coil, the transformer is said to be stepping down the voltage. This is known as a step-down transformer. The voltage level in the secondary coil is lower than the voltage level in the primary coil, which makes it safer for use in residential and commercial buildings. This is why step-down transformers are commonly used in the distribution of electrical power to homes and businesses.
The process of stepping up or stepping down voltage in an electrical transformer is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current flows through the primary coil, it creates a changing magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary coil. The voltage level in the secondary coil is determined by the ratio of the number of turns in the primary coil to the number of turns in the secondary coil.
One of the key advantages of electrical transformers is their efficiency. They are able to transfer electrical energy with minimal loss, which helps to keep energy costs low. Additionally, electrical transformers are also able to transfer electrical energy over long distances, which is crucial for the transmission and distribution of electricity.
In conclusion, electrical transformers are devices that are used to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. They play a crucial role in the transmission and distribution of electricity, and one of the most important functions of an electrical transformer is its ability to step up or step down voltage levels. This is achieved through the ratio of the number of turns in the primary coil to the number of turns in the secondary coil. Transformers are efficient devices that help to keep energy costs low and enable the transmission of electrical energy over long distances.