Working principle of DC motor
We know that a motor is a device that transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. In the case of DC motor, it’s one type of motor that uses the DC current to convert electrical energy to mechanical energy.
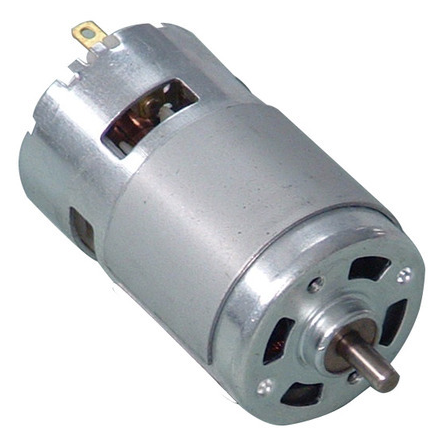

Working principle of DC motor
Actually, the motor principle based on Faraday’s Law which states that it is the conversion of electrical and mechanical energy.
All the electro-mechanical developments we see around us are caused either by an A.C. or on the other hand a DC engine. Here we will investigate this sort of engine. This is a device that converts DC electrical to mechanical energy.
At the point when a current-carrying conductor is put in a magnetic field, it encounters a torque and tends to move. It is known as a motoring activity. If the direction of current in the wire is reversed, the direction of rotation also reverses.
At the point when the magnetic field and electric field connect they deliver mechanical power, and in light of that the working rule of the DC engine set up.
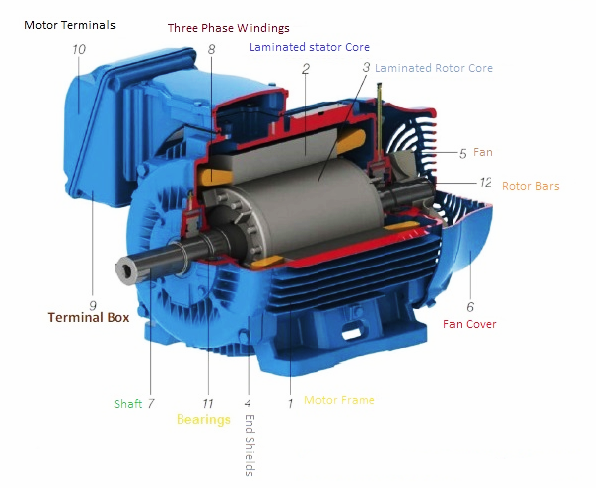
DC motor consist of the following things:
- Rotor
- Stator
- Air gap
- Winding
- Commutator
The DC motor can be categorized as
- Shunt Motor
- Separately Excited Motor
- Series Motor
- Permanent Magnet motor
- Compounded Magnet motor
Examples of DC motors are Fans, household appliances, blowers and pumps, and so on.
The advantage of the DC motor
- Easy to control speed in a wide range
- Traction and the servo motors use the DC motors
- Comfortable to use, as its dimensions permit considerable space-saving.
The disadvantage of the DC motor
- DC engine creates low weight condition; that is the reason it can’t be utilized for artificial hearts. On the off chance that we utilize this for artificial hearts, we need to transform it inside 60 minutes.
- Relative to AC engines, DC engines are costly.